Edexcel A
level Chemistry (2017)
Topic 11:
Equilibrium II:
Here is
the first learning objective:
1. To be able to deduce an expression for Kp, for homogeneous and
heterogeneous systems, in terms of equilibrium partial pressures in atmospheres.
Mathematical skills that could be developed in this topic include
constructing expressions for Kc and Kp and calculating values with relevant
units, estimating the change to the value of an equilibrium constant when a
variable changes.
Calculating Kp
for an homogenous equilibrium:
Kp
is the equilibrium constant expressed in terms of partial pressures.
The
partial pressure of a gas is the
pressure of a gas in a mixture of gases that the gas would exert if it alone
occupied the space.
The
partial pressure of a gas depends on the gas’s mole fraction in its mixture.
For
example:
Given
we have the partial pressures of each gas in a homogenous equilibrium we can
then use each value to calculate the equilibrium constant Kp.
For
the homogenous ammonia equilibrium system:
N2(g) +
3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g)
Partial
pressures are:
pN2 =
2.31 atm
pH2 =
4.62 atm
pNH3 = 8.08
atm
So
calculating Kp
Determining
the units of Kp in this
example:
this
reduces down to
For
a heterogenous equilibrium only the
species in the gaseous state affect the equilibrium.
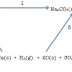
e.g.
CaCO3(s) ⟶ CaO(s) +
CO2(g)
so
the decomposition of calcium carbonate depends on the partial pressure of
carbon dioxide in the kiln.
Kp =
pCO2 Units of Kp are Atmospheres (atm)
since all other reacting species are in the solid state and do not exert a partial pressure.












No comments:
Post a Comment