How to build neutralisation equations
If combustion equations
present us with problems to solve them so do neutralisation equations
Did you know there are at least two types of
neutralisation equation?
Essentially neutralisation
occurs when an acid neutralises a base or an alkali (an alkali being a water soluble base)
Here are three typical
neutralisation equations:
First
Hydrochloric acid + sodium
hydroxide = sodium chloride + water
HCl + NaOH
= NaCl
+ H2O
This is an example of an acid neutralising a water soluble base
(alkali)
Second
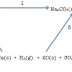
Nitric acid + sodium carbonate = sodium nitrate + water + carbon
dioxide
HNO3 +
Na2CO3 = NaNO3 + H2O + CO2
This is an example of an acid plus an insoluble base i.e. a
carbonate
Third
Sulfuric acid +
magnesium oxide = magnesium sulphate + water
H2SO4 + MgO = MgSO4 + H2O
This is an example of an acid plus an insoluble base i.e. a metal
oxide
So how do we construct and balance these kinds of
equations?
A) Let’s look at the first example: acid and soluble
base
How can we build an equation for the reaction between
say nitric acid and potassium hydroxide?
Let’s put the words down first:
This is the pattern:
Acid +
soluble base = water +
soluble salt
Nitric acid + potassium
hydroxide = ????
Next add the formulas of the
two reactants so:
Nitric acid +
potassium hydroxide = ?????
HNO3 +
KOH =
Now notice that water forms
so remove the elements of water from the
reactants.
I have highlighted these elements
so
Nitric acid +
potassium hydroxide = ?????
HNO3 + KOH =
These will combine to form one water molecule
Nitric acid +
potassium hydroxide = water
HNO3 + KOH = H2O
The remaining parts of the
reactants form the soluble salt potassium nitrate
Nitric acid +
potassium hydroxide = water
+ potassium nitrate
HNO3 + KOH = H2O + KNO3
With a diprotic acid like
sulphuric acid things gets a little trickier
B) Let’s look at a second example: acid and insoluble
base a metal oxide
How can we build an equation for the reaction between
sulfuric acid and copper oxide?
Let’s put the words down
first:
This is the pattern:
Acid +
insoluble metal oxide = water
+ soluble salt
sulfuric acid +
copper oxide = ????
Next add the formulas of the
two reactants so:
sulfuric acid +
copper oxide = ????
H2SO4 + CuO
Now notice that water forms
so remove the elements of water from the
reactants.
I have highlighted these
elements so
sulfuric acid +
copper oxide = ????
H2SO4 + CuO
These will combine to form one water molecule
sulfuric acid +
copper oxide = water
H2SO4 + CuO = H2O
The remaining parts of the
reactants form the soluble salt copper sulfate
sulfuric acid +
copper oxide = water + copper sulfate
H2SO4 + CuO = H2O + CuSO4
With a monoprotic acid like
nitric acid things gets a little trickier
C) Let’s look at a third example: acid and insoluble
base a metal carbonate
How can we build an equation for the reaction between
nitric acid and magnesium carbonate?
Let’s put the words down
first:
This is the pattern:
Acid +
insoluble metal carbonate = water
+ carbon dioxide + soluble salt
nitric acid + magnesium carbonate = ????
Next add the formulas of the
two reactants so:
nitric acid + magnesium carbonate = ????
HNO3 +
MgCO3 =……….?
Now notice that water and carbon dioxide form so remove the elements of water and carbon
dioxide from the reactants.
I have highlighted these
elements so
nitric acid + magnesium carbonate = ????
HNO3 +
MgCO3 =……….?
These will combine to form one carbon dioxide molecule but there
is not enough hydrogen for a water molecule, so we have to double up the nitric
acid formulas.
nitric acid + magnesium carbonate = water
+ carbon dioxide
2HNO3 +
MgCO3 = H2O + CO2
The remaining parts of the
reactants form the soluble salt magnesium nitrate and note that there are now two nitrates to one magnesium
Note too that the nitrates are placed in brackets
with the 2 outside to show the magnesium to nitrate ratio is 1:2.
nitric acid + magnesium
carbonate = water + carbon dioxide + magnesium carbonate
2HNO3 + MgCO3 = H2O + CO2
+ Mg(NO3)2
You need to be able to make
yourself familiar with as many examples like these as you can imagine for
example:
Nitric acid +
sodium hydroxide
Sulphuric acid + potassium hydroxide
Hydrochloric acid +
ammonium hydroxide
Sulphuric acid +
ammonium hydroxide
Nitric acid +
copper oxide
Nitric acid +
zinc oxide
Nitric acid +
iron (III) oxide
Sulfuric acid +
magnesium oxide
Sulphuric acid +
sodium oxide
Sulphuric acid +
iron (II) oxide
Hydrochloric acid +
copper oxide
Hydrochloric acid +
iron (II) oxide
Hydrochloric acid +
magnesium oxide
Nitric acid +
copper carbonate
Sulphuric acid +
potassium carbonate
Hydrochloric acid +
ammonium carbonate etc……….







No comments:
Post a Comment