3. What are the Properties of Halogenalkanes?
A: Physical properties
i) Why are halogenoalkanes polar molecules?
The diagram shows the
halogen atom (X) is slightly more negative than the carbon atom.
The reason
for this is the difference in electronegativity between the halogen and the
carbon atom.
This difference occurs in
all haloalkanes except the iodo– and astato– versions.
The iodine and astatine atom
have electronegativities similar or lower than that of carbon.
ii) How do we know haloalkanes reflect the isotopic abundance
of chlorine and other halogens?
The relative abundance of
these elements is reflected in the mass spectra of the compounds:
For example:
Chloroethane
CH3CH235Cl :
CH3CH237Cl
3 : 1
Note the relative heights of
the peaks at 64 and 66 at 3:1 reflecting the relative abundance of naturally
occurring chlorine.
Bromomethane
CH379Br : CH381Br
1 : 1
The two molecular ion peaks are at 94 and 96
amu of fairly equal abundance because that pattern is true of naturally
occurring bromine.
iii) How do we know haloalkanes
have molecular structures?
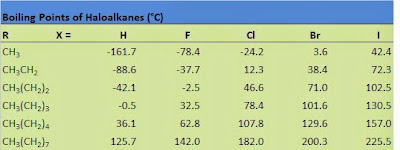
We see that all haloalkanes
have relatively low melting and boiling points which point to their molecular
structure.
These bps are the result of weak intermolecular forces.
The intermolecular forces
here are Van der Waals forces and dipole – dipole interactions.











No comments:
Post a Comment