Reactions of the
Halogenoalkanes
How does competition
between substitution and elimination reactions in haloalkanes work out?
What we find is this:
A) In ethanol solvent where OH— acts as a base rather
than a nucleophile then the corresponding alkene forms by elimination of HBr like this:
CH3CH2CH2CH2Br +
OH— =
CH3CH2CH=CH2 + H2O + Br—
1-bromobutane base but-1-ene
B) But if the solvent is
changes for water then the substitution
reaction dominates as the hydroxide ion
acts as a nucleophile in the more
polar solvent:
CH3CH2CH2CH2Br + OH— = CH3CH2CH2CH2OH + Br—
1-bromobutane butan-1-ol
The important point to
remember is that both substitution and
elimination mechanisms occur together.
The use of a solvent favours one over the other but does not mean that
one works exclusively instead of the other.
So ethanolic potassium hydroxide allows the elimination mechanism to predominate
Aqueous potassium hydroxide favours the substitution
mechanism in the haloalkane.
I have discussed the
substitution mechanism here
The elimination mechanism is
a concerted mechanism, one step following on the next…
First, the base abstracts a proton attached to the carbon atom attached to
the C—Br bond.
Second, the two electrons remaining from the C—H bond
form a double carbon-carbon bond
Third, these two electrons repel the electrons in the
C—Br bond (rather than the C—CH3 bond) because the bromine atom
forms a good leaving group as a bromide ion (Br—).
The result is an alkene see
below:
In this example,
2-bromo-2-methyl propane is converted into methylpropene.
You should be able to see
why this is called an elimination
reaction.
HBr is removed (eliminated)
from the haloalkane molecule (It is
product and should be in the equation).
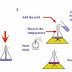
The experiment can be
carried out in the laboratory by use of a simple test tube apparatus collecting
the gaseous alkene over water.
You should be able to draw
the apparatus used as it is essentially the same kit as that used below in
cracking liquid paraffin.
You should of course be able
accurately to add labels to your diagram
You should be able to give
the equation for the reaction of 2-bromobutane and ethanolic KOH in which two
different alkenes are formed.
You should be able to name
and draw the displayed formulae of these two alkene products.








No comments:
Post a Comment