Edexcel A level
Chemistry (2017)
Topic 15:
Principles of transition metal chemistry
Learning Objectives related to vanadium chemistry
15/20. To know what the colours of the oxidation states of vanadium (+5,
+4, +3 and +2) are in its compounds.
15/21. To understand the redox reactions for the inter-conversion of the
oxidation states of vanadium (+5, +4, +3 and +2), in terms of the relevant Eo values.
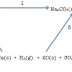
Some Vanadium Chemistry
Vanadium
has several stable oxidation states at room temperature.
Vanadium
(II) V2+ purple
Vanadium
(III) V3+ green
Vanadium (IV) VO2+ blue
Vanadium
(V) VO2+ yellow
Each of
these states can exist in a redox equilibrium with the one below in acid
solution.
Each
redox equilibrium has its own redox potential.
You add
these to an oxidation number chart or redox potential chart.
Here they
are:
V3+(aq) + e— ⟶ V2+(aq) Eo = —0.26v
[VO2+(aq) + 2H+(aq)] + e— ⟶ V3+(aq) + H2O(l) Eo = +0.34v
[VO2+(aq) + 2H+(aq)]
+ e— ⟶ [VO2+(aq)
+ H2O(l)] Eo = +1.00v
Reduction of Vanadium(V) to
Vanadium(II)
As the
zinc/zinc(II) reduction potential is —0.76v then addition of zinc amalgam (zinc
dissolved in mercury) or zinc powder to a solution of vanadium(V) ions will
bring about a reduction of the yellow vanadium(V) eventually to purple
vanadium(II).
3Zn(s) + 2VO2+(aq)
+ 8H+(aq) ⟶ 2V2+(aq)
+ 4H2O(l) + 3Zn2+(aq)
yellow purple
Reduction of Vanadium(V) to
Vanadium(III)
Adding
tin powder should reduce the vanadium(V) to vanadium(III) since the tin/tin(II)
reduction potential lies at —0.14v.
2Sn(s) + 2VO2+(aq)
+ 8H+(aq) ⟶ 2V3+(aq)
+ 4H2O(l) + 2Sn2+(aq)
yellow green
Reduction of Vanadium(V) to
Vanadium(IV)
Adding
iodide ions to a solution of vanadium(V) will reduce the vanadium(V) down to
vanadium(IV) since the iodine/iodide reduction potential lies at +0.54v.
I—(aq) + VO2+(aq)
+ 2H+(aq) ⟶
VO2+(aq) +
H2O(l) + ½I2(aq)
yellow blue brown
However
the resultant brown colour of the product iodine will mask the blue of
vanadium(IV).
To remove
this brown colour add thiosulphate ions.
I2(aq) +
2S2O32—(aq) ⟶ 2I—(aq) + S4O62—(aq)
brown colourless








No comments:
Post a Comment