To recall the simple chemical test for halide ions Cl— (aq), Br— (aq) and I— (aq) in aqueous solution .
The Halogens form a group of non- metals on the right hand side of the
Periodic Table Group 7 next to the noble gases.
There are three particular chemical reactions that most courses include.
The reaction of halogens with metals
The reaction of halogens with non – metals
The reaction of halogens with halide ions
Then there is the simple chemical test for halide ions.
The simple chemical test for halide ions: Cl—(aq),
Br—(aq), I—(aq).
These are precipitation reactions.
To see if an aqueous salt
solution contains halide ions first add a few drops of dilute nitric acid
followed by a few drops of 0.05M silver nitrate solution (AgNO3 (aq)).
The nitric acid is there to
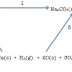
remove any other ions particularly carbonate ions that would also form a
precipitate with silver nitrate since silver carbonate is a white insoluble solid.
The silver ions in the silver
nitrate solution form insoluble precipitates with chlorides, bromides and
iodides.
With Chlorides:
Silver nitrate forms a white
precipitate with chlorides.
AgNO3 (aq) +
NaCl(aq) ⟶ AgCl(s) +
NaNO3 (aq)
White ppt
The ionic equation:
Ag+ (aq) +
Cl—(aq) ⟶ AgCl(s)
With Bromides:
Silver nitrate forms a cream
precipitate with bromides.
AgNO3 (aq) +
NaBr(aq) ⟶ AgBr(s) +
NaNO3 (aq)
Cream ppt
The ionic equation:
Ag+ (aq) +
Br—(aq) ⟶
AgBr(s)
With Iodides:
Silver nitrate forms a yellow
precipitate with iodides.
AgNO3(aq) +
NaI(aq) ⟶ AgI(s) +
NaNO3(aq)
Yellow
ppt
The ionic equation:
Ag+ (aq) +
I—(aq) ⟶ AgI(s)
Further confirmatory tests:
If the white precipitate of
silver nitrate is added to dilute
ammonia solution it should dissolve.
If the cream precipitate of
silver bromide is added to concentrated
ammonia solution it should dissolve
And yellow silver iodide
should be found to be insoluble in
ammonia solution.
Effect of bright
sunlight
Lastly, if the three
precipitate are exposed to bright light or sunlight then after a few minutes
the white precipitate of silver chloride turns dark purple, the bromide turns
dark green and the iodide remains yellow.
Summary
Summary
The video below shows these
tests:








No comments:
Post a Comment