Esterification is a reaction in organic chemistry that mirrors acid
+base = salt + water in inorganic chemistry
Alcohol + Organic acid
= Ester +
Water
Dr Carr’s Rescue Box: Naming
Esters
This is where the examiner will make a sustained effort
to
catch you out.
He knows that naming esters is tough for even the best
candidates.
So how will we beat him?
A bit of counter-intuitive thinking is needed from us. I
mean thinking backwards!!
Here is an ester structural formula CH3CH2COOCH3
How do we name it?
First find the –COO- group.
Note the alkyl groups either side, here we’ve an ethyl CH3CH2—
and a methyl CH3—
The ethyl is attached to the C of the COO group so
that's the acid from which the ester’s named in this case 3 carbons or
propanoic acid
The other alkyl group fronts up the name that is:
Methylpropanoate.
The conditions require the use of strong acid catalyst
such as concentrated sulphuric acid (H2SO4) or
hydrochloric acid (HCl).
The method is basically to heat the mixture of alcohol
and organic acid and strong acid catalyst under reflux.
Then distill off the ester product.
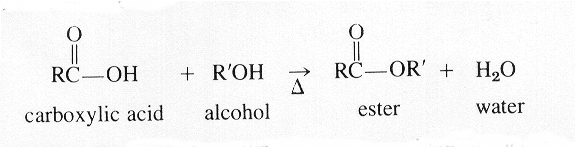
Here is typical reaction:
Both these equations correctly show that the water forms from the hydrogen of the alcohol and the —O—H of the carboxyl group.
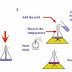
A less complicated method is illustrated here:
Once the mixture has been heated for a few minutes it can be poured into sodium carbonate solution to neutralise the acid catalyst leaving us to smell the ester.











No comments:
Post a Comment