Amines
AQA
Amines are
compounds based on ammonia where alkyl or aryl groups replace the hydrogen
atoms. This section includes their reactions as nucleophiles.
Preparation of
Amines
Primary aliphatic
amines can be prepared by the reaction of ammonia with halogenoalkanes and by
the reduction of nitriles.
Aromatic amines,
prepared by the reduction of nitro compounds, are used in the manufacture of
dyes.
OCR:6.2.1b
(b) the preparation of:
. (i) aliphatic amines
by substitution of haloalkanes with excess ethanolic ammonia and amines
. (ii) aromatic amines by
reduction of nitroarenes using tin and concentrated hydrochloric acid.
Including
formation of primary amines from ammonia and secondary/tertiary amines from
amines.
See also reduction of nitriles (see
6.2.4 c).
Edexcel:
Topic 18B 11 and 12
11. To understand, in terms of
reagents and general reaction conditions, the preparation of primary aliphatic
amines:
. i from
halogenoalkanes
. ii by the
reduction of nitriles
12. To know that aromatic
nitro-compounds can be reduced, using tin and concentrated hydrochloric acid,
to form amines
Preparation
of aliphatic amines
1) Reaction
of ammonia with a halogenoalkane (haloalkane)
Treat a
primary haloalkane with ethanolic ammonia and “initially the conjugate acid of
the corresponding primary amine is formed” to quote ROC Norman:
H3N:↷CH3—I
→ H3N+—CH3 +
I—
The
conjugate acid can then react with further ammonia to form the primary amine
and the ammonium ion.
CH3—NH3+ +
NH3 ⇋ CH3—NH2 + NH4+
However
the primary amine that has just been formed will then react with a second
molecule of the halogenoalkane and this reaction will lead to the formation of
the secondary amine
CH3—NH2 +
CH3—I → (CH3)2+NH2
+
I—
The
secondary amine can them react with further excess haloalkane and produce the
tertiary amine.
Usually
a mixture of products finally forms so that we can say the alkylation of
ammonia is a less than satisfactory method of the formation of amines.
A
little modification of the method means that it can be used to form the primary
amine. A good yield of primary amine is
obtained if a considerable excess of ammonia is used since to quote ROC Norman
again “the amine formed is a relatively ineffective competitor for reaction
with the halide”.
2)
Reduction of the corresponding nitrile
Nitriles
can be reduced catalytically using finely divided nickel and hydrogen under
pressure at about 150oC.
To
prevent the formation of secondary amine, ammonia is added to the nitrile flow.
Benzyl
cyanide (phenyl methyl nitrile) gives phenyl ethyl amine at 85% yield in liquid
ammonia under pressure.
Ni/H2/NH3
PhCH2CN -------→ PhCH2CH2NH2
120oC 120atm
This
is reduction reaction the addition of hydrogen to the nitrile across its triple
bond.
Preparation
of aromatic amines
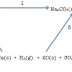
Aromatic
amines can be prepared by the reduction of aromatic nitro compounds like
nitrobenzene (C6H5NO2) which forms phenylamine
(or aniline) C6H5NH2
This
is one long preparation and complex involving steam distillation and
purification of the organic product.
The
exam specs just expect you to know of the reaction and to be able to articulate
the equation for the prep.
Next
up we look at the properties of amines:..








No comments:
Post a Comment