C5.3 Equilibria
Summary
Common misconceptions
In a reaction, when the rate
of the forward reaction equals the rate of the backwards reaction, the reaction
in a closed system is said to be in equilibrium.
Learners often do not
recognize that when a dynamic equilibrium is set up in a reaction the
concentration of the reactants and products remain constant. They think that
they are equal. Learners also sometimes perceive a dynamic equilibrium as two
reactions.
Underlying knowledge and
understanding
Learners will be familiar with
representing chemical reactions using formulae and using equations.
C5.3a To recall that some
reactions may be reversed by altering the reaction conditions
C5.3b To recall that dynamic
equilibrium occurs in a closed system when the rates of forward and reverse
reactions are equal
Higher tier:
C5.3c To be able to predict
the effect of changing reaction conditions on equilibrium position and suggest
appropriate conditions to produce as much of a particular product as possible
Le Chatelier’s principle
concerning concentration, temperature and pressure
Ammonia and Equilibria
For many
years, chemists have illustrated how changing conditions: temperature,
concentration and pressure, affect the position of chemical equilibrium using
ammonia production by the Haber Process.
First, what is ammonia?
Ammonia is a
gas at r.t.p.
It is very
soluble in water: 1ml of water can dissolve 777ml of ammonia gas. You can watch ammonia and the fountain experiment
here.
Bromothymol blue is the indicator, blue in alkali.
Bromothymol blue is the indicator, blue in alkali.
Ammona is toxic
It is less
dense than air at 0.73kg/m3 (Air
= 1.225 kg/m3)
Ammonia is a weak
alkali
NH3 +
H2O ⇌
NH4+
+ OH—
As a weak
alkali, it can neutralise common acids and form soluble salts that find use as
water soluble fertilisers, as example would be ammonium nitrate: NH4NO3
NH4OH +
HNO3 ⟶ NH4NO3 + H2O
As an alkali
it is also used in low concentrations as a treatment for stings and bites e.g.
from ants and/or nettles because the stinging agent is formic/methanoic acid
HCOOH.
It is used as
a “mordant” in hair dye: remember the corny British hair dye advert that used
Penelope Cruz speaking the strapline “No ammonia!!”
Ammonia is formed
from covalent molecules.
The bonding
is covalent. The bonds between nitrogen and hydrogen are pairs of shared
electrons.
Its
structure is simple molecular. The discrete
groups of atoms are loosely bonded to each other with very weak van der Waals
forces.
The effect
of forming ammonia is to fix nitrogen from its molecular form (N2 ) into an
accessible molecular form that plants can absorb through their root
systems. Most plants ( except legumes) cannot absorb molecular nitrogen from the air and absorb it through their roots in the form of ammonia and ammonium ions and nitrate ions.
Second, fixing nitrogen in ammonia.
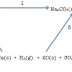
Nitrogen is fixed
into ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen using the Haber process.
The Haber
process is an equilibrium reaction.
N2(g) +
3H2(g) ⇌
2NH3 (g)
⇌
this sign indicates not just a reversible reaction but an equilibrium state.
In these reactions, the rate
of the forward reaction equals the rate of the backwards reaction, but the
reaction must be in a closed system
for it to be said to be in equilibrium.
A closed
system is a reaction vessel in which nothing can get in and nothing can get out, like a stoppered bottle in the diagram below.
Look at a reagent bottle half full of water at room temperature.
Inside the sealed bottle there are two processes happening simultaneously.
Water molecules from the liquid state enter the gaseous state at the rate
r1.
Simultaneously, water molecules from the gaseous water vapour enter the
liquid state at the identical rate r2.
r1 = r2
How do we know that r1 = r2?
The water level never changes at constant temperature.
If we left the bottle on the lab bench for 10,000 years the water level
would remain the same at constant temperature (that’s unlikely by the way given
the rate of enhanced global warming!!)
And yet the water level is constantly changing its composition as molecules
leave and enter the liquid state!!!
The level looks static yet it is changing all the time!!.
The contents of the bottle look static yet they are in dynamic equilibrium.
The water molecules (billions upon billions of them it has to be said) are
in constant motion entering and leaving the liquid state.
The concentration of water in the bottle never changes of course.
This is what it is if the volume of water is 500ml.
500ml weighs 500g at r.t.p. because water’s density is 1g/cm3.
The molar mass of water is 18 g/mol.
So the number of moles of water is 500/18 = 27.78 moles.
That's for half a litre of water so the concentration of water in moles per
litre will be 27.78 × 2 = 55.6M.
The concentration of water [H2O] = 55.6M
and is constant at constant temperature.
But the
concentration of the water vapour is very much lower than this.
The two
species, water and water vapour, are not at the same concentration even though
we are looking at an equilibrium system.
However, the two opposing rates of evaporation and condensation are equal to each other
r1 = r2.
All these conditions are true only if the stopper remains on the bottle but
take it out and there is no longer a sealed system and no longer a perfect
dynamic equilibrium.
These are the exclusive features of all perfect dynamic equilibria.
• constant temperature (think about what would happen if the bottle
above was stood in a beaker of boiling water)
• sealed system (no material leaves or enters the reaction)
• equal and opposite reaction rates
• unchanging constant concentrations of reactants and products
(sometimes referred to as the position of equilibrium)
Many reactions are reversible but very few exist in a perfect equilibrium
state.
Chemists often assume the perfect equilibrium state exists for a
reaction when in reality a very imperfect one exists especially in industrial
processes where material is constantly being added at the start and removed at
the end of the process!!
Let’s look
now at the effect of temperature and pressure on the ammonia equilibrium and
how the optimum conditions are created for its production.
We will use
a practical principle that helps us decide the effect of changing conditions. Henri
Louis le Chatelier, a French chemical engineer, first explained the principle back
in the 1880’s.
Le Chatelier said:
Le Chatelier said:
“When a stress is applied to a system in
equilibrium, the position of equilibrium shifts is such a way so as to absorb
the change.”
Here’s how
it works out:
A: The effect of temperature change on the
ammonia equilibrium
N2(g) +
3H2(g) ⇌
2NH3 (g)
The forward
reaction in this equilibrium—making ammonia—is exothermic and heat is given out
(92kJ/mole to be precise).
So if we
make the equilibrium hotter raising its temperature, Le Chatelier tells us that
the equilibrium will seek to resist this change.
It will
change so as to make things cooler by favouring the backwards reaction i.e. the
decomposition of ammonia—not its formation.
This means that at higher temperatures there is a lower yield of
ammonia.
This effect
is not what we expect since we all think that if we warm up a chemical reaction
we will create more product but not so here in this reaction.
B: The effect of change of pressure on the
ammonia equilibrium
More
molecules N2(g) +
3H2(g) ⇌
2NH3 (g) less
molecules
The pressure
exerted by a gas is a result of collisions of molecules with the surface of the
container they are in. You can see from
the equation that the forward reaction—making ammonia— leads to fewer molecules
in the reaction vessel.
Now if we
raise the pressure on the equilibrium Le Chatelier tells us that it will resist
this imposed change. The equilibrium
will move its position to lower the pressure and that must mean fewer molecules
in the reaction vessel and that must means more ammonia is produced at higher
pressures.
Higher
pressures bring about greater yields of ammonia as they favour the forward
reaction.
We can see
the effect of changing pressure and temperature on the yield of ammonia in the
graph below:
C: Creating the optimum (best) conditions for the
production of ammonia.
N2(g) +
3H2(g) ⇌
2NH3 (g)
First, a
reasonably safe and cost effective pressure is used. Too high risks explosion and also means
greater expense in building an industrial plant to withstand a very high (say
800 atmos) pressure.
Second, a
temperature is used that is also cost effective but not so low as to make the
reactions of both forward and backward too slow and unprofitable. So we use 400oC.
Third, to
ensure that the reaction goes fast enough at this optimum temperature a finely
divided, high surface area iron (Fe) catalyst is used. The catalyst does not increase or decrease
the ammonia yield but it does ensure the yield is achieved in as short a time
as possible.
You can see
the optimum conditions pointed out on the graph above.